Advantages of a 1031 Exchange

Advantages of a 1031 Exchange
The main advantage of a 1031 exchange
One of the main advantages of an exchange is that an investor/taxpayer can use their entire equity to acquire a replacement property. Property exchangers who have held onto properties for decades due to tax consequences have the option of moving their equity into more beneficial properties.
Exchange transactions can be tax-free with future taxes deferred. Purchasing like-kind property through an exchange is generally preferable to buying and selling.
It is not uncommon for investors to buy real estate in order to leverage their investment and gain appreciation using "someone else's" money, such as an institutional lender, a seller who finances part of the purchase price, or on the basis of tax savings when exchanging under I.R.C. § 1031.
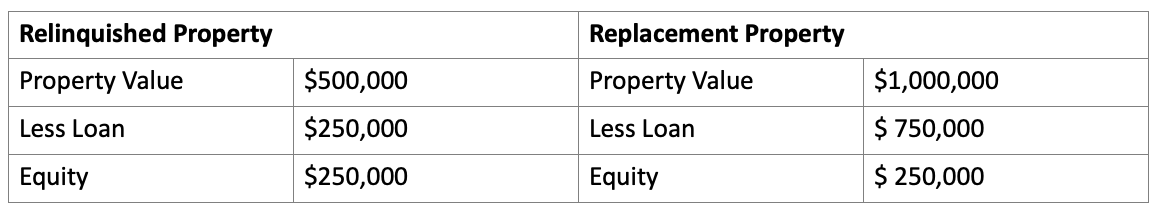
A $500,000 property was leveraged into a $1,000,000 property in Example 1. An investor made the down payment using equity that would otherwise have been taxed. To acquire the $1,000,000 replacement property, the taxpayer had to increase the amount owed:
Example 1
Investments in raw land are often made by investors. Raw land, however, is usually a cash drain because of property taxes. It is up to the taxpayer to decide when and how to dispose of such investment property.
There are times when raw land (farmland, and under-improved properties) does not generate any cash relative to its fair market value. Using a 1031 exchange can help an investor avoid the tax on gain when trading into a cash-flowing asset.
Investors might decide to diversify one desirable property investment into two or more smaller, newer properties in different neighborhoods. Maintenance costs may be lower, vacancies may be lower, and appreciation may be greater for such properties.
Investors who have acquired various properties over time may decide to replace them with a single property with equal or greater value than the value of the separate properties combined. Management fees may be saved by this consolidation.
Investors who relinquish non-depreciable property (raw land) for depreciable replacement property (apartment building) will benefit from shifting the substituted tax basis from non-depreciable property to depreciable property if the replacement property has a higher ratio of depreciable fair market value to total fair market value than the relinquished property's depreciable tax basis to total tax basis.
Based on the fair market value of its components, the replacement property's basis is allocated accordingly. With a 1031 exchange, the exchange can be tax deferred.
Investors may want to relocate, but not become absentee landlords. A taxpayer can relocate any income-producing property, whether residential or commercial.
The IRS 1031 exchange can be used to manage the sale and purchase of an investment property that would be costly from a tax standpoint. An investor relocating through an exchange may avoid the old state's income tax on the gain altogether (with some exceptions).
